The fall of Roman empire
For more than a millennium, Rome dominated most of Europe and the Mediterranean region. But starting about 200 AD, the Roman Empire’s internal operations started to deteriorate. Rome was faltering under the weight of its enormous empire by the year 400 AD. In 476 AD, Rome ultimately collapsed.
The fall of Roman empire

The fall of Roman empire
The Peak of Roman Power
Under the leadership of the renowned Roman emperor Trajan, Rome reached its zenith in the second century, or approximately the year 117 AD. The Roman Empire ruled over almost the whole Mediterranean coastline. Northern Africa, Palestine, Egypt, southern Britain, Italy, France, and Spain were all included in this.
Gradual Decline
The fall of Rome was a gradual process that took place over a long period of time. The empire started to fall apart for a variety of reasons. The following are a few reasons why the Roman Empire fell:
- The politicians and rulers of Rome became more and more corrupt
- Infighting and civil wars within the Empire
- Attacks from barbarian tribes outside of the empire, such as the Visigoths, Huns, Franks, and Vandals.
- The Roman army was no longer a dominant force
- The empire became so large it was difficult to govern
Rome Divides into Two
Emperor Diocletian concluded in AD 285 that the Roman Empire was too large to oversee. He separated the Roman Empire into two halves: the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. Rome would split into three sections, then back into two, and rejoined a few times during the next century or so. Ultimately, the empire was permanently divided into two in AD 395. Rome dominated the Western Empire, while Constantinople ruled the Eastern Empire.
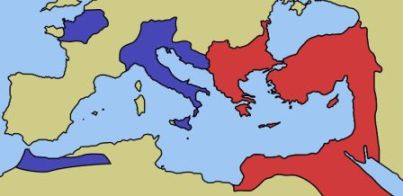
The Western Roman Empire, which Rome dominated, is the subject of this discussion’s “fall” of Rome. After a thousand years, the Eastern Roman Empire was renamed the Byzantine Empire and continued to rule.
The City of Rome is Sacked
Many believed that Rome could not be conquered. But the Visigoths, a Germanic barbarian clan, overran the city in 410 AD. They demolished numerous structures, slaughtered and sold many Romans into slavery, and plundered the valuables. This was the first time Rome had been taken over in eight centuries.
Rome Falls
Rome was taken over by a Germanic barbarian named Odoacer in AD 476. He ascended to the throne of Italy and compelled Romulus Augustulus, the final emperor of Rome, to abdicate. This is regarded by many historians as the fall of the Roman Empire.
The Dark Ages Begins
Europe underwent numerous transformations with the fall of Rome. Rome has contributed a robust educational system, culture, and government. Europe has now become largely barbaric. Europe’s next 500 years would come to be known as the Dark Ages.
Facts about The fall of Roman empire
- The Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantium, fell in 1453 to the Ottoman Empire.
- Many poor people were glad to see Rome fall. They were starving to death while being taxed heavily by Rome.
- Near the end of the Roman Empire, the city of Rome was no longer the capital. The city of Mediolanum (now Milan) was capital for a while. Later, the capital was moved to Ravenna.
- Rome was sacked once again in 455 AD by Geiseric, King of the Vandals. The Vandals were an Eastern Germanic tribe. The term “vandalism” comes from the Vandals.
Read also:Barbarians in Ancient Rome
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
