Housing and Homes in Ancient Rome
Depending on their level of affluence, the Romans inhabited a wide range of houses. The impoverished were housed in tiny shacks in the countryside or small apartments in the metropolis. The wealthy resided in opulent country mansions or private residences in urban areas.

Housing and Homes in Ancient Rome
Homes in the City
The majority of people in Ancient Rome’s cities resided in flats known as insulae. The size of the single-family dwellings known as domus, which the wealthy inhabited, varied according to their wealth.
Insulae
Most Roman city dwellers were housed in insulae, which were small apartment complexes. Insulae typically held between thirty and fifty people and were three to five floors high. Typically, each individual unit had two compact rooms.
Shops and stores that opened out into the streets were frequently located on the lowest floor of the insulae. The tiniest flats were at the top, while the bigger ones were close to the bottom. A large number of insulae have poor construction. If they caught fire, they might be dangerous locations; occasionally, they might even collapse.
Private Homes
The massive single-family residences known as domus were inhabited by the rich aristocracy. The insulae were not nearly as lovely as these houses. The rooms and features of most Roman homes were the same. The atrium, the principal room of the home, was accessible through an entryway. The kitchen, dining area, and bedrooms may be located off the sides of the atrium. The office was located beyond the atrium. There was usually an open garden at the back of the house.
Here are some of the rooms in a typical Roman house: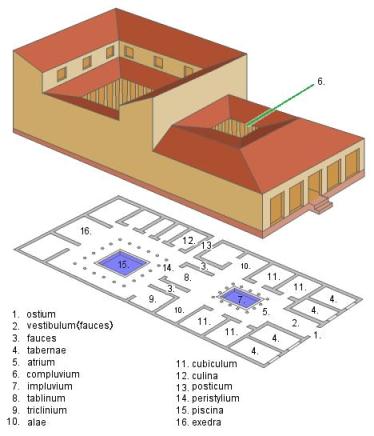
- Vestibulum: A grand entrance hall to the house. On either side of the entrance hall might be rooms that housed small shops opening out to the street.
- Atrium: an open room where guests were greeted. The atrium typically had an open roof and a small pool that was used to collect water.
- Tablinum: The office or living room for the man of the house.
- Triclinium: The dining room. This was often the most impressive and decorated room of the house in order to impress guests that were dining over.
- Cubiculum: The bedroom.
- Culina: The kitchen.
Homes in the Country
The wealthy inhabited enormous, wide homes known as villas, while the impoverished and slaves resided in little shacks or cottages in the countryside.
Roman Villa
A wealthy Roman family’s villa was often far bigger and cozier than their city residence. In addition to servants’ quarters, they had courtyards, bathrooms, swimming pools, storage areas, fitness centers, and gardens. They also included contemporary conveniences like heated flooring and indoor plumbing.
Facts About the Homes of Ancient Rome
- The word “insulae” means “islands” in Latin.
- The entrance to a Roman house was called the ostium. It included the door and the doorway.
- Fine Roman homes were built with stone, plaster, and brick. They had tiled roofs.
- A “villa ubana” was a villa that was fairly close to Rome and could be visited often. A “villa rustica” was a villa that was a far distance from Rome and was only visited seasonally.
- Wealthy Romans decorated their homes with murals, paintings, sculptures, and tile mosaics.
Read also: Roman baths History and facts
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
