Gods of Ancient Egyptian
Learn about Ancient Egyptian Gods and Goddesses. The history of this world civilization.

Gods of Ancient Egyptian
Overview
Ancient Egyptian culture heavily emphasized religion. They had faith in many different gods and goddesses. These deities might manifest in many ways, generally as animals. Depending on the location, temple, or time period, a single animal may stand in for several different deities.
Major Gods and Goddesses
Some gods and goddesses were more significant and well-known than others. The following are a few of the more significant ones:
Gods of Ancient Egyptian
The most revered god among the Ancient Egyptians was Ra, the sun god. He was depicted as a guy with a hawk head and a sun disk on his headgear. Ra and the other god Amun were once joined to create the even more potent Amun-Ra. Ra was the supreme ruler of the gods and was credited with creating all life forms.
Isis
The mother goddess was Isis. She was regarded as someone who would defend and assist those in need. She was shown as a female with a crown in the form of a throne.
Osiris
God of the dead and lord of the underworld, Osiris. He was the father of Horus and the husband of Isis. A mummified man wearing a feathered headdress was shown as Osiris.
Horus
The god of the sky was Horus. Isis and Osiris had a son named Horus. He was shown as a man with a hawk’s head. Pharaoh, the Egyptian king, was revered as the living embodiment of Horus. In this way, Pharaoh served as the head of Egyptian religion and the gods’ emissary to the people.
Thoth
The god of wisdom was Thoth. He bestowed writing, medicine, and mathematics upon the Egyptians. He was also the moon’s god. Thoth is shown as a man with the head of an Ibis bird. He was sometimes depicted as a baboon.
Temples
Several Pharaohs erected enormous temples in praise of their deities. Large statues, gardens, memorials, and a place of worship would all be present in these temples. For their own native gods, towns would also have their own temples.
The Luxor Temple, the Isis Temple at Philae, the Temples of Horus and Edfu, the Temples of Rameses and Nefertiti at Abu Simbel, and the Temple of Amun at Karnak are a few well-known temples.

Was Pharaoh considered a god?
Pharaoh was regarded by the Ancient Egyptians as their primary representative with the gods; he may have served as a high priest more so than a god. He was nevertheless strongly linked to the god Horus and might perhaps have been regarded as a god in human form.
Afterlife
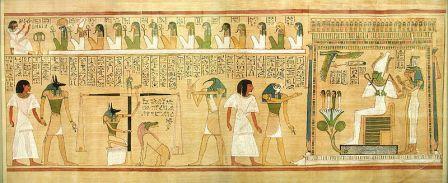
The Book of the Dead – Drawn on the walls of a tomb
by Jon Bodsworth
The Egyptians had a belief in life after death. They believed that persons were made up of two key components: a “ba,” which was more akin to a soul, and a “ka,” or life force, which existed only while a person was alive. The individual would reside in the hereafter if the “ka” and “ba” could merge there. For this to occur, the body’s preservation was a necessary element. For this reason, the Egyptians preserved the dead by the process of mummification, or embalming.
Read also: Entertainment of Ancient Egypt
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
