Geography of Ancient Greece
Geography of Ancient Greece
Learn about Geography of Ancient Greece and Aegean Sea, mountains, islands, regions, and important cities in Ancient Greece and how they impacted the growth of Greek culture.
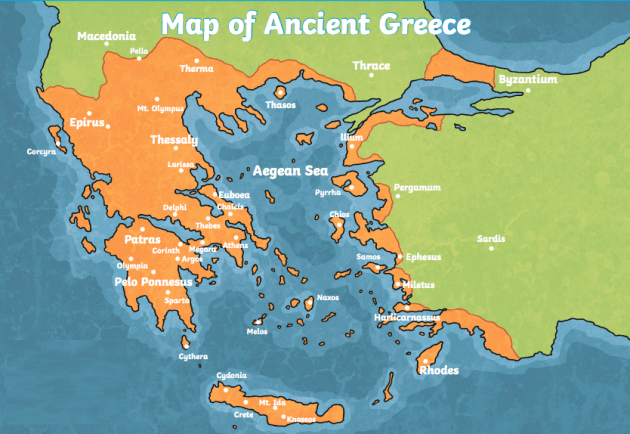
Greece’s ancient civilization existed along the Mediterranean Sea coast in southeast Europe. The terrain of the area influenced the ancient Greeks’ political system and way of life. The Greeks were compelled to live along the coast as a result of geographical formations like mountains, oceans, and islands creating natural barriers between the Greek city-states.
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is the name of the area of the Mediterranean where the Greeks initially made their home. Greek city-states developed all along the Aegean Sea’s shoreline and on its numerous islands. Greece’s inhabitants traveled from city to city by using the Aegean. Fish was also available for consumption in the Aegean.
Mountains
Greece’s landscape is covered in mountains. Mountains cover around 80% of the Greek mainland. Long-distance land travel was rendered challenging as a result. Additionally, the mountains served as a natural boundary between the largest city-states. Mount Olympus is the tallest mountain in Greece. The Twelve Olympians, according to ancient Greek belief, were the gods who resided atop Mount Olympus.
Islands
More than 1000 islands can be found in the Aegean Sea. Many of these islands, including the largest island, Crete, as well as Rhodes, Chios, and Delos, were colonized by the Greeks.
Climate
Ancient Greece typically experienced warm summers and mild winters. Most individuals wore light clothing for the most of the year because it was so hot. During the chilly winter days, they would put on a cloak or wrap.
Regions of Ancient Greece
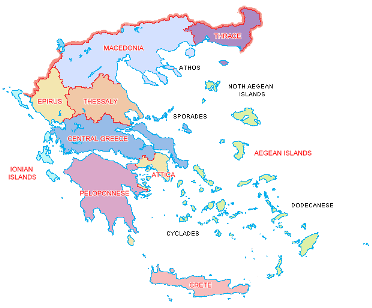
Regions of Greece
The mountains and seas of Ancient Greece formed several natural regions:
- Peloponnese – The Peloponnese is a large peninsula located at the southern tip of the Greek mainland. It is almost an island and only connects to the main land by a small strip of land called the Isthmus of Corinth. The Peloponnese was home to several major Greek city-states including Sparta, Corinth, and Argos.
- Central Greece – Just north of the Peloponnese is Central Greece. Central Greece was home to the famous region of Attica and the city-state of Athens.
- Northern Greece – Northern Greece is sometimes broken up into three major regions including Thessaly, Epirus, and Macedonia. Mount Olympus is located in Northern Greece.
- Islands – Major groupings of the Greek islands include the Cyclades Islands, the Dodecanese, and the Northern Aegean Islands.
Major Cities
The Ancient Greeks spoke the same language and had similar cultures. They were not one large empire, however, but were divided into a number of powerful city-states such as Athens, Sparta, and Thebes.
Greek Settlements
The Greeks set up colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. This included settlements in modern-day Italy, France, Spain, Turkey, and parts of North Africa. These colonies helped to spread the Greek culture throughout the region.
Facts About the Geography of Ancient Greece
- The Greeks called their land “Hellas.” The English word “Greece” comes from the Roman word for the country “Graecia.
- Under the rule of Alexander the Great, Greece expanded into a large empire that included Egypt and stretched all the way to India.
- The Pindus Mountain Range runs north to south along much of mainland Greece. It is sometimes called the “spine of Greece.
- The Greek philosopher Plato once said that “we live around the sea like frogs around a pond.
Read also : Timeline of Ancient Greece
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
