Central African Kingdoms: History and Facts
A sizable portion of Central Africa is covered in savanna grasslands and rainforests. This area has been inhabited by humans for thousands of years. In what is now Chad and Cameroon, the Sao Civilization was one of the first to flourish here. As early as 500 BCE, the Sao civilization was established. Other Central African kingdoms came and went over time. Below, we’ll talk about a few of the important kingdoms.

Central African Kingdoms: History and Facts
Kingdom of Zimbabwe

In the year 1200 CE, the Kingdom of Zimbabwe rose to power and ruled for more than two centuries. It was situated in what is now the nation of Zimbabwe. The renowned metropolis of Great Zimbabwe stood at the heart of the kingdom. At its height, Great Zimbabwe was a sizable city with 18,000 residents, according to estimates. For a long time, it served as the hub of trade and authority in Central and Southern Africa. Great Zimbabwe’s massive stone walls and towers are still intact today.
Kingdom Kongo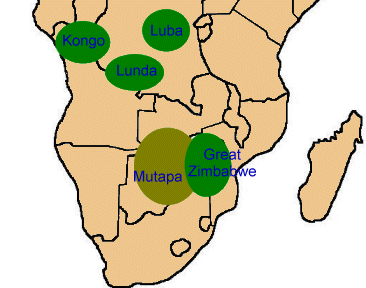
By the end of the 1300s, the Kongo Kingdom became powerful. Up until 1914, it governed a sizable portion of Central Africa before becoming a Portuguese colony. The Monikongo was the name of the Kongo ruler. The Portuguese landed in 1483. They carried trade links and Christianity with them. The slave trade was also carried out by them. Slave trafficking eventually started to undermine the Kongo. Afonso I of Manikongo was one of the rulers that made an effort to put an end to the slave trade. They didn’t succeed, though. The kingdom was in decline by the late 1800s, and in 1914 the Portuguese seized control of it.
Kingdom Luba
In 1585, the Kingdom of Luba was established in Central Africa. Up until 1889, it reigned over a sizable portion of what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. A king known as the Mulpwe and an elder council known as the Bamfumus oversaw Luba. Llunga Mbili was Luba’s first king. Kalala Llunga, his eldest son, was regarded as the greatest Luba ruler. Tshibinda Llunga, his second son, established the Lunda Kingdom.
Kingdom Lunda
Tshibinda Llunga, the brother of the King of Luba, founded the Lunda Kingdom in 1665. By subduing neighboring tribes and capturing territory, the Lunda grew farther east. With a governing king and a council, the Lunda’s government was quite similar to the Luba’s. The Kingdom kept expanding until the arrival of European powers and their colonization of the area in the late 1800s.
Kingdom Mutapa
The modern-day nations of Zimbabwe and Mozambique were part of the Kingdom of Mutapa, which governed a sizable portion of Central Africa. A warrior chief from the Kingdom of Zimbabwe founded it for the first time in 1430. Through the trade of ivory and gold mining, the kingdom expanded and prospered. In the 1500s, it established economic ties with Portugal. Following the king’s death in 1759, civil war broke out, which led to the dissolution of the kingdom.
Facts about the Kingdoms of Central Africa
- Some of the most valuable items in Central Africa were dried fish, cloth, and salt.
- It is thought that Great Zimbabwe extended its trade network as far as China and the Middle East.
- The people of Central Africa mostly speak the Bantu languages and are often called the Bantu peoples.
- Swahili is a Bantu language. You have likely heard some Swahili words such as “simba”, which means lion, and “safari”, which means journey.
Central African Kingdoms: History and Facts
Read also: Aksum Kingdom History and Facts
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
