Aksum Kingdom History and Facts
An ancient African country was the country of Aksum. It is occasionally referred to as Ancient Ethiopia or the Kingdom of Axum.

Aksum Kingdom History and Facts
Where was the Kingdom of Aksum located?
The Red Sea’s southern coast was home to the Kingdom of Aksum. Aksum occasionally controlled parts of the Arabian Peninsula to the east of the Red Sea, but the majority of the empire lay on the Horn of Africa, west of the Red Sea. The kingdom included most of what is now Eritrea, as well as Yemen, Sudan, northern Ethiopia, and southern Saudi Arabia.
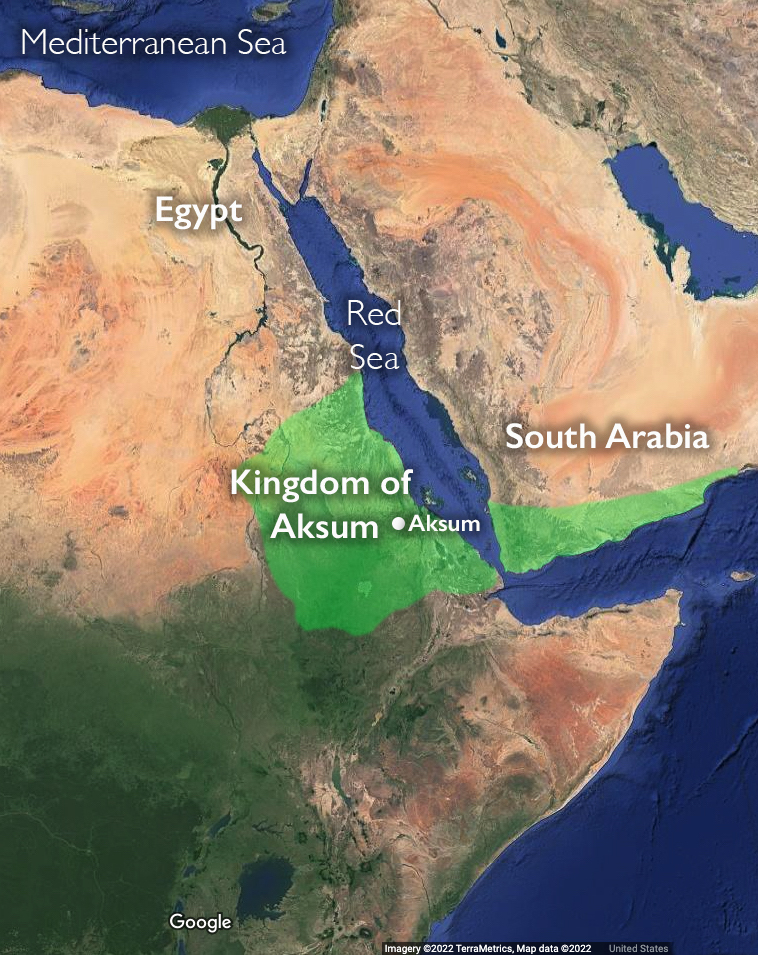
How long did the Kingdom of Aksum rule?
Aksum most likely came into being in 400 BCE. According to legend, the son of Israel’s King Solomon and Queen Sheba founded the kingdom initially. Around 100 CE, Aksum started to gain strength and grow; it peaked around 350 CE. Up until a foreign queen overthrew it in 940 CE, it remained the dominant force in the area. Following a phase of instability, the Zagwe Dynasty seized authority over the area.
King Ezana and the Peak of the Aksum Empire
Under the direction of King Ezana, who ruled from roughly 325 to 360 CE, Aksum achieved its pinnacle. Aksum grew in size and developed into a significant trading hub throughout this period. King Ezana was in charge when Aksum overthrew the Kingdom of Kush and destroyed Meroe. King Ezana became a Christian as well. Being a devoted Christian, he helped establish Christianity as the dominant religion in the kingdom.
Center of Trade
Aksum was in an ideal location to grow into a significant trading hub. To trade, traders would travel to Aksum with their commodities from Egypt, Persia, India, and central Africa. A number of commercial routes, including important waterways like the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden, and the Nile River, were accessible to Aksum.
Situated on the Red Sea coast, the city of Adulis served as Aksum’s principal port. Adulis traders dealt in a broad range of goods, including salt, gold, ivory, gemstones, textiles, glass, and olive oil. To purchase commodities at Adulis, some traders would journey from far-off places like the Roman Empire and India.
Culture of the Kingdom of Aksum
Owing to its geographic location and its significance in global trade, Aksum’s culture evolved into a synthesis of numerous regional civilizations. The Arabs, Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians all had an impact on them. Following 325 CE, Christianity emerged as the dominant religion, and it too had a significant cultural impact.
One of the more developed African cultures at the time was Aksum. They created their own coinage and a written language. Additionally, they invented irrigation and terraced farming, which increased the productivity of their steep land by enabling people to cultivate the nearby mountains’ slopes.
Architecture and Towers
In contrast to their Egyptian counterparts to the north, Aksum did not construct pyramids. Rather, Aksum is well-known for its stelae, or lofty towers. The tallest of these structures was close to one hundred feet. Fake windows, stone doorways, and inscriptions were all beautifully carved into the towers. The Obelisk of Axum, which was captured by Italian forces in 1937 when they conquered Ethiopia, is the most well-known of these towers. Later, in 2008, the tower was rebuilt using the sections that had been returned.
Facts about the Kingdom of Aksum
- The city of Axum still exists in northern Ethiopia. It is a fairly small city with a population of just over 50,000 people. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Africa.
- The stone buildings in Aksum were built without the use of mortar. Instead, the stones were carved to fit snugly together.
- The city of Adulis was destroyed by Islamic invaders in 710. This isolated Aksum and began its decline.
- With merchants from all around the world coming to Aksum to trade, Greek was generally used as the common language.
Read also: Kingdom of Kush History and Facts
 The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
The First Encyclopedia Your First Knowledge Home
